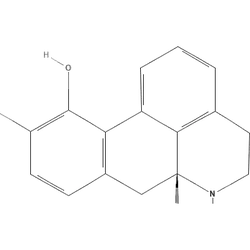
Summary
Apomorphine is primarily used to treat acute hypomobility episodes in advanced Parkinson's disease. Despite its name, it does not contain morphine and does not bind to opioid receptors. Nausea is extremely common; antiemetic pretreatment with trimethobenzamide or domperidone is typically required. Contraindicated with 5-HT3 antagonists due to severe hypotension risk. Contains sulfites which may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Dose Information
| ROA | Light | Common | Strong | Heavy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sublingual | 10mg | - | - | - |
Light
Common
Strong
Heavy
Onset, Duration & After-effects
| ROA | Onset | Comeup | Peak | Offset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous | 5-20 min | 10-15 min | 20-60 min | 30-60 min |
| Sublingual | 10-30 min | 15-30 min | 30-90 min | 30-60 min |
Tolerance
Build-up
develops within days of regular use; analgesic tolerance faster than respiratory depression tolerance
Reset
7–14 days for partial reset; full reset may take weeks — tolerance loss greatly increases overdose risk
Effects
Positive
- Relief of Parkinsonian symptoms
- Stimulation
Negative
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Increased heart rate
- Vasoconstriction
- Insomnia
- Yawning
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Sudden sleep onset
Positive
- Alertness enhancement
- Euphoria
- Wakefulness
- Motivation enhancement
Negative
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Anxiety
- Compulsive behaviors
- Talkativeness
- Time distortion
Positive
- Increased music appreciation
- Increased libido
- Tactile enhancement
- Color enhancement
Negative
- Light sensitivity
- Appetite suppression
- Dehydration
- Disinhibition
- Hallucinations
- Drifting